- 704
- HENGLU NEWS
2'-Fucosyllactose (2’-FL) is one of the most abundant and functionally significant human milk oligosaccharides (HMOs) found in human milk. To understand its importance, it is essential to first explore the broader category it belongs to, human milk oligosaccharides. Human milk oligosaccharides are a complex group of indigestible carbohydrates that play a crucial role in the health and development of infants. They represent the third largest solid component of human milk, following fat and lactose. In colostrum, which is the first milk produced after childbirth, human milk oligosaccharides are found in concentrations ranging from 22-24 g/L. In mature milk, their levels typically range from 5-12 g/L. In contrast, human milk oligosaccharides are found in very low concentrations in cow’s milk and other mammalian milk, highlighting the unique composition of human milk.
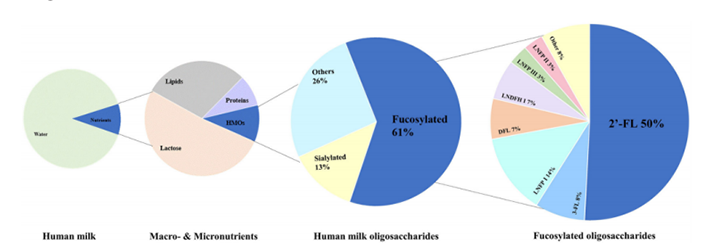
Currently, researchers have identified more than 200 different types of human milk oligosaccharides in human milk. Of these, the structures of nearly 100 have been thoroughly analyzed and categorized. Human milk oligosaccharides can be classified based on their monosaccharide composition and structural characteristics into four main categories: neutral fucosylated, neutral non-fucosylated, sialylated, and other human milk oligosaccharides. Among these, neutral fucosylated human milk oligosaccharides, such as 2'-Fucosyllactose, stand out due to their abundance and significant health benefits. Its prevalence in human milk, along with its important role in infant health, has spurred significant research, leading to the approval of 2'-Fucosyllactose for use in infant formula, dietary supplements, and medical foods by both the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Union.
The history of 2'-Fucosyllactose research stretches over several decades. Advances in biochemical techniques and analytical methods have been critical in uncovering its structure and function. Below is a brief history of the significant milestones in the study of 2'-Fucosyllactose.
The journey began in 1954 when Polonowski, Lespagnol, and Montreuil used two-dimensional paper chromatography to identify two forms of fucosyllactose—2'-Fucosyllactose and 3-Fucosyllactose—in human milk. This discovery laid the foundation for further exploration into the complex world of human milk oligosaccharides. In 1967, Grollman and Ginsburg made a crucial observation regarding 2'-Fucosyllactose. They found that this particular human milk oligosaccharide was undetectable in the milk of women who were non-Secretors, a genetic trait affecting the presence of certain carbohydrates in bodily fluids. Building on this, Kobata in 1969 developed a new method to identify and characterize oligosaccharide patterns using smaller milk samples, advancing the ability to study 2'-Fucosyllactose more accurately. In the 1980s, Egge and colleagues applied a range of sophisticated analytical methods, including high-performance thin-layer liquid chromatography (HPLC), mass spectrometry (MS), and H-NMR spectroscopy, to analyze fucose-containing human milk oligosaccharides like 2'-Fucosyllactose. These techniques allowed scientists to achieve more precise separation and quantification of these complex molecules. By 1994, advances in mass spectrometry, specifically MALDI-TOF, significantly improved the detection and quantification of human milk oligosaccharides, allowing for more detailed profiles of milk glycans. This development was a turning point in human milk oligosaccharides research, facilitating the comprehensive analysis of 2'-Fucosyllactose in human milk. More recently, in 2013, researchers described a new method for resolving and quantifying neutral oligosaccharides, including 2'-Fucosyllactose. Using graphitic carbon high-performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry, they were able to simultaneously measure a range of oligosaccharides with great precision, adding to the growing understanding of 2'-Fucosyllactose and its role in human milk.
2'-Fucosyllactose is not just a structural component of human milk; it plays a dynamic role in enhancing infant health and development. Here are some of the key functions of 2'-Fucosyllactose:
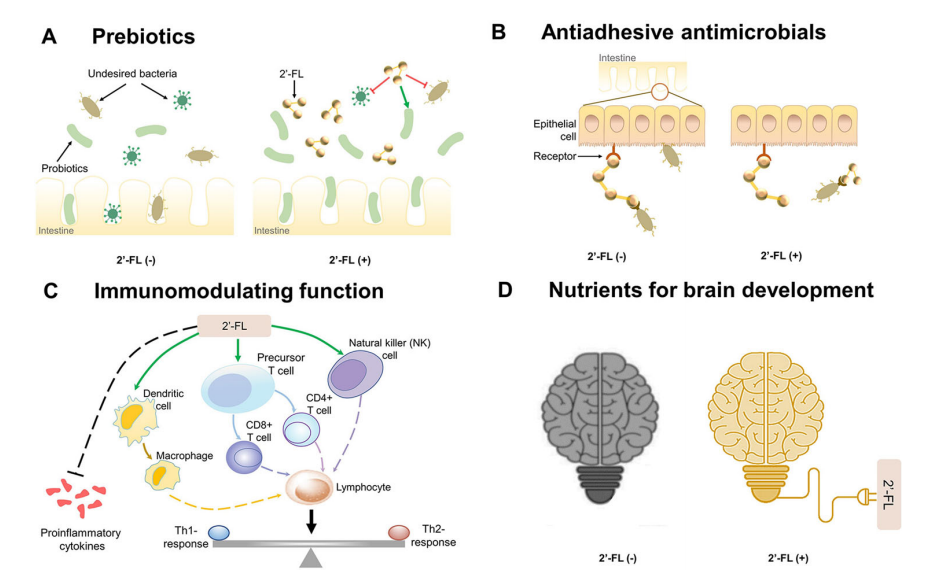
Promotion of Intestinal Probiotics and Inhibition of Harmful Bacteria
One of the most important roles of 2'-Fucosyllactose is in the gut. Infants are born with an immature digestive system, and the colonization of beneficial bacteria, such as Bifidobacteria, is crucial for the development of a healthy gut microbiota. 2'-Fucosyllactose acts as a probiotic, promoting the growth of these beneficial bacteria while simultaneously inhibiting the proliferation of harmful bacteria, such as Escherichia coli and Clostridium difficile. By fostering a healthy microbial balance, 2'-Fucosyllactose contributes to better digestion, nutrient absorption, and overall gut health.
Prevention of Pathogenic Bacterial Adhesion
2'-Fucosyllactose plays a critical role in preventing pathogenic bacteria from adhering to the epithelial cells that line the infant’s gut. Many pathogens, such as Salmonella and Campylobacter, attempt to bind to fucose-containing receptors on these cells to initiate infection. 2'-Fucosyllactose acts as a decoy receptor, mimicking these binding sites and thus preventing pathogens from adhering to the gut lining. This anti-adhesion property is a key mechanism through which 2'-Fucosyllactose protects infants from gastrointestinal infections.
Immune System Modulation and Anti-inflammatory Effects
In addition to its effects on the gut microbiome, 2'-Fucosyllactose also modulates the immune system. It has been shown to support the maturation of immune cells and enhance immune responses. Furthermore, 2'-Fucosyllactose helps to regulate inflammation by reducing pro-inflammatory cytokine production, which can protect against conditions such as necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC), a severe inflammatory disease that affects the intestines of premature infants.
Cognitive and Neurological Development
Emerging research suggests that 2'-Fucosyllactose may play a role in brain development and cognitive function. Human milk oligosaccharides, including 2'-Fucosyllactose, have been found to cross the blood-brain barrier, where they may influence neurodevelopmental processes. Studies in animal models have shown that 2'-Fucosyllactose can promote learning, memory, and overall brain structure development. While human studies are still ongoing, the potential for 2'-Fucosyllactose to support cognitive development makes it an exciting area of research.
2'-Fucosyllactose is a remarkable component of human milk, playing critical roles in the health and development of infants. From promoting beneficial gut bacteria to protecting against pathogens, regulating the immune system, and supporting brain development, 2'-Fucosyllactose is a key player in early-life nutrition. The timeline of its discovery and the evolution of analytical methods that have allowed scientists to study it in detail show how far research has come. Today, the incorporation of 2'-Fucosyllactose into infant formulas and medical foods underscores its importance in supporting infant health, particularly for those who are not breastfed. As science continues to unravel the full spectrum of its benefits, 2'-Fucosyllactose remains a shining example of the incredible complexity and functionality of human milk.
Citation:
[1]Shi, R., & Jiang, Z. Q. (2020). Progress and prospect of enzymatic synthesis of 2’-fucosyllactose. Synthetic Biology, 1(4), 481.
[2] Zhu, Y., Wan, L., Li, W., Ni, D., Zhang, W., Yan, X., & Mu, W. (2022). Recent advances on 2′-fucosyllactose: physiological properties, applications, and production approaches. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 62(8), 2083–2092.
[3] Li, N., Xu, K., Li, L., Yu, H., & Xu, Z. (2021). Research progress on physiological efficacy and preparation methods of 2’-fucosyllactose. Food and Fermentation Industry, 47(23), 265-271.
[4] Castanys‐Muñoz, E., Martin, M. J., & Prieto, P. A. (2013). 2′‐fucosyllactose: an abundant, genetically determined soluble glycan present in human milk. Nutrition Reviews, 71(12), 773–789.



