- 500
- HENGLU NEWS
Human milk oligosaccharides (HMOs) are a complex group of oligosaccharides found in breast milk, representing the third most important solid component. They interact with other bioactive compounds and play various essential physiological roles.
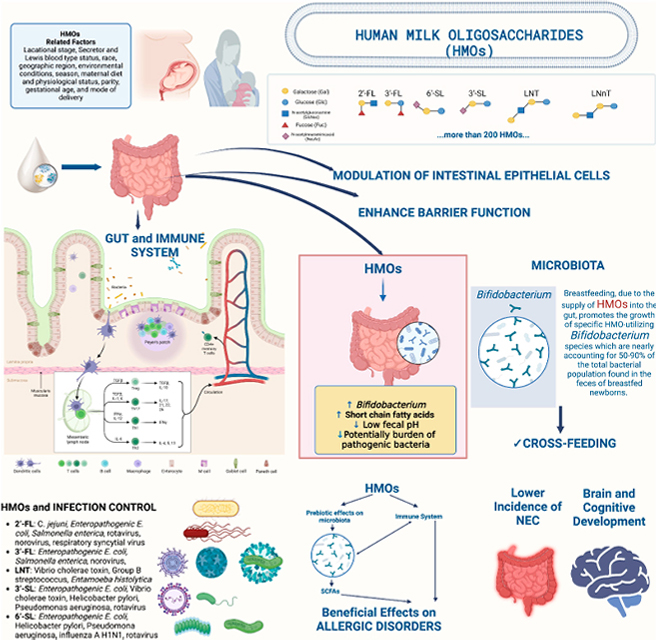
Human milk oligosaccharides can enhance the gastrointestinal barrier, helping to protect the gut from harmful substances. Human milk oligosaccharides also promote the growth of beneficial bacteria, such as Bifidobacteria, maintaining the balance of the gut microbiome, which has a positive effect on gut health.
While human milk oligosaccharides are primarily associated with infants, increasing research suggests they may also positively impact adult health.
Supporting Digestive Health:
Human milk oligosaccharides act as prebiotics, encouraging the growth of beneficial bacteria and maintaining the balance of gut microbiota. This can help prevent or alleviate digestive issues, such as diarrhea or constipation.
Boosting the Immune System:
Human milk oligosaccharides are believed to help regulate the immune system, reduce inflammatory responses, and strengthen the body’s resistance to pathogens, lowering the risk of infectious diseases.
Anti-Adhesion Properties:
Human milk oligosaccharides have anti-adhesion properties, which can prevent pathogenic bacteria from adhering to the surface of intestinal cells. This reduces the colonization and proliferation of harmful bacteria in the gut, helping to protect against infections.

Impact on Neurological Development:
Human milk oligosaccharides positively affect brain and nervous system development and function, supporting cognitive function and emotional health.
In today’s society, as research on human milk oligosaccharides advances, HMO-containing products may be viewed as supplements for regulating the gut microbiome in adults. With the popularization of health and weight-loss ideals, many people pursue weight loss, sometimes through unscientific methods that may harm health.
Healthy weight loss requires a comprehensive approach, and dietary regulation is essential as it directly impacts metabolism and energy consumption. Human milk oligosaccharides can promote the growth of beneficial bacteria in the gut, especially increasing Bifidobacteria, thereby reducing the need for antibiotics, improving metabolism, and aiding in effective fat loss. Additionally, human milk oligosaccharides support weight loss by inhibiting the growth of harmful bacteria and the formation of toxic metabolites, promoting intestinal motility, reducing excessive water absorption, and alleviating constipation.
Human milk oligosaccharides are expected to be a promising health supplement, helping to regulate the gut microbiome, promote metabolism, and relieve constipation, thereby enhancing overall health. Further research on the mechanisms and biological functions of human milk oligosaccharides can deepen our understanding of their roles in gut health and weight management, providing scientific insights for developing related products and personalized health management plans.



